

Detection and characterization of abnormal b220+ lymphocyte subsets in lpr/lpr and dominant-negative Fas transgenic mice by 4- and 5-color flow cytometric analysis.
Up to five fluorescent parameters can be analyzed simultaneously on the Vantage. In the example below, mouse T splenocytes were phenotyped with FITC-conjugated antibodies against CD4, PE-anti-Fas, PerCP-anti-surface IgG and IgM (all excited by the 488 nm argon laser line), APC-anti-CD3 (excited by the 632 nm HeNe laser line) and AMCA-anti-b220 (excited by the 351 nm argon laser line). The cytograms below show most possible 2-D combinations for the analyzed parameters. Using 5-color analysis it is possible to simultaneously determine the level of Fas expression on all of the phenotyped T and B lymphocyte types and the development of abnormal lymphocyte subsets (such as b220+CD3+Ig-CD4-CD8- lymphocytes in lpr/lpr mice). The protocol below was designed in collaboration with Dr. Elizabeth Lacy and Tonya Villafana at Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center to access abnormal lymphocyte development in lpr/lpr and dominant-negative Fas transgenic mice, and to detect and characterize new abnormal lymphocyte subsets in these animals. Dr. Lacy is also using 4-color analysis on the FACSCalibur to monitor the lymphocyte phenotype of these transgenic mice.
(Below). An example of a 5-color experiment. Fluorescent immunophenotyping includes FITC-anti-CD4, PE-anti-Fas, PerCP-anti-IgM, APC-anti-CD3 and AMCA-anti-b220.
(Below). The structure of 7-amino-3-(((succinimidyl)oxy)carbonyl)methyl)-4-methylcoumarin-6-sulfonic acid (AMCA-S-NHS). This UV-excited fluorochrome can be conjugated to antibodies and used for 5 color immunophenotyping using the 351 nm line of the Vantage argon laser. It's sulfonic acid group makes it more water-soluble than many amine-reactive forms of AMCA, making it more suitable for protein conjugation. We prepare antibody conjugates using this reagent (from Molecular Probes). Click here for the labeling protocol we use.
7-amino-3-(((succinimidyl)oxy)carbonyl)methyl)-4-methylcoumarin-6-sulfonic acid (AMCA-S-NHS)
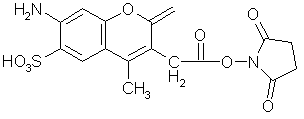
(Below). Excitation and emission spectra of AMCA. Excitation (dotted line) and emission spectra (solid line) are shown. AMCA can be excited by the 351 nm line of our argon laser (indicated by the arrow). Jackson ImmunoResearch makes AMCA-conjugated secondary antibodies and avidin and has a data sheet on the fluorochrome.
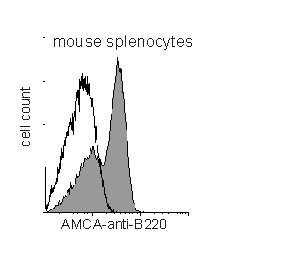
(Below). Detection of b220 on mouse B lymphocytes using AMCA-conjugated anti-mouse b220 antibody. A histogram showing mouse B cell b220 expression using AMCA-conjugated antibodies prepared by us in the Flow Core. Most UV-excitable fluorochromes are more weakly fluorescent than those excited by visible light such as FITC. Strongly expressed antigens (such as b220) should therefore be chosen for AMCA conjugation. Talk to us for more information about custom conjugations.
(Below). Detection of Fas on B6 mouse thymocytes using biotinylated anti-Fas monoclonal antibody (Jo2) followed by AMCA-avidin. Immunodetection of antigens using AMCA can be enhanced using either a secondary antibody system or avidin-biotin, but should still be used only with strongly expressed markers.
Back to the HSS Flow Cytometry Core Facility Home Page.